Effects of Water Pollution?
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies (like oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, aquifers, and groundwater) usually caused due to human activities. Water pollution is any change, minor or major in the physical, chemical or biological properties of water that eventually leads to a detrimental consequence of any living organism. Drinking water, called Potable Water, is considered safe enough for human and animal consumption.

On human health:
Water pollution kills. In fact, it is causing millions of deaths across the world every year. Contaminated water can also make you ill. Every year, unsafe water sickens about 1 billion people. And low-income communities are disproportionately at risk because their homes are often closest to the most polluting industries.
Waterborne pathogens, in the form of disease-causing bacteria and viruses from human and animal waste, are a major cause of illness from contaminated drinking water. Diseases spread by unsafe water include cholera, giardia, and typhoid. Even in wealthy nations, accidental or illegal releases from sewage treatment facilities, as well as runoff from farms and urban areas, contribute harmful pathogens to waterways.
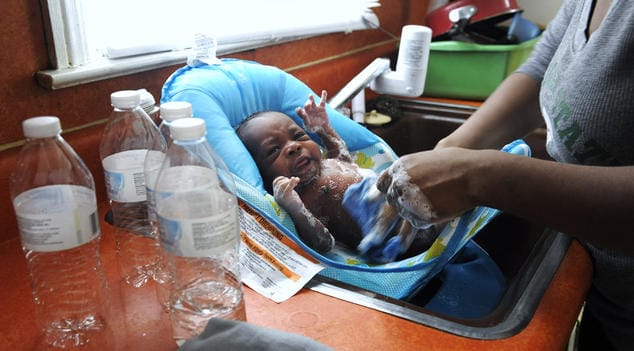
A woman using bottled water to wash her three-week-old son at their home in Flint, Michigan
Meanwhile, the plight of residents in Flint, Michigan—where cost-cutting measures and aging water infrastructure created the recent lead contamination crisis—offers a stark look at how dangerous chemical and other industrial pollutants in our water can be. The problem goes far beyond Flint and involves much more than lead, as a wide range of chemical pollutants—from heavy metals such as arsenic and mercury to pesticides and nitratefertilizers—are getting into our water supplies. Once they’re ingested, these toxins can cause a host of health issues, from cancer to hormone disruption to altered brain function. Children and pregnant women are particularly at risk.
Even swimming can pose a risk. Every year, millions of people contract health issues such as skin rashes, pinkeye, respiratory infections, and hepatitis from sewage-laden coastal waters, according to EPA estimates.
On the environment:
In order to thrive, healthy ecosystems rely on a complex web of animals, plants, bacteria, and fungi—all of which interact, directly or indirectly, with each other. Harm to any of these organisms can create a chain effect, imperilling entire aquatic environments.
When water pollution causes an algal bloom in a lake or marine environment, the proliferation of newly introduced nutrients stimulates plant and algae growth, which in turn reduces oxygen levels in the water. This dearth of oxygen, known as eutrophication, suffocates plants and animals and can create “dead zones,” where waters are essentially devoid of life. In certain cases, these harmful algal blooms can also produce neurotoxins that affect wildlife, from whales to sea turtles.
Chemicals and heavy metals from industrial and municipal wastewater contaminate waterways as well. These contaminants are toxic to aquatic life—most often reducing an organism’s life span and ability to reproduce—and make their way up the food chain as predator eats prey. That’s how tuna and other big fish accumulate high quantities of toxins, such as mercury.
Marine ecosystems are also threatened by marine debris, which can strangle, suffocate, and starve animals. Much of this solid debris, such as plastic bags and soda cans, gets swept into sewers and storm drains and eventually out to sea, turning our oceans into trash soup and sometimes consolidating to form floating garbage patches. Discarded fishing gear and other types of debris are responsible for harming more than 200 different species of marine life.
Meanwhile, ocean acidification is making it tougher for shellfish and coral to survive. Though they absorb about a quarter of the carbon pollution created each year by burning fossil fuels, oceans are becoming more acidic. This process makes it harder for shellfish and other species to build shells and may impact the nervous systems of sharks, clownfish, and other marine life.
Common Types of Water Contamination:
Sewage and wastewater:
Used water is wastewater. It comes from our sinks, showers, and toilets (think sewage) and from commercial, industrial, and agricultural activities (think metals, solvents, and toxic sludge). The term also includes stormwater runoff, which occurs when rainfall carries road salts, oil, grease, chemicals, and debris from impermeable surfaces into our waterways

More than 80 percent of the world’s wastewater flows back into the environment without being treated or reused, according to the United Nations; in some least-developed countries, the figure tops 95 percent. In the United States, wastewater treatment facilities process about 34 billion gallons of wastewater per day. These facilities reduce the amount of pollutants such as pathogens, phosphorus, and nitrogen in sewage, as well as heavy metals and toxic chemicals in industrial waste, before discharging the treated waters back into waterways. That’s when all goes well. But according to EPA estimates, our nation’s aging and easily overwhelmed sewage treatment systems also release billions of gallons of untreated wastewater each year.
Oil pollution:
Big spills may dominate headlines, but consumers account for the vast majority of oil pollution in our seas, including oil and gasoline that drips from millions of cars and trucks every day. Moreover, nearly half of the estimated 1 million tons of oil that makes its way into marine environments each year comes not from tanker spills but from land-based sources such as factories, farms, and cities. At sea, tanker spills account for about 10 percent of the oil in waters around the world, while regular operations of the shipping industry—through both legal and illegal discharges—contribute about one-third. Oil is also naturally released from under the ocean floor through fractures known as seeps.
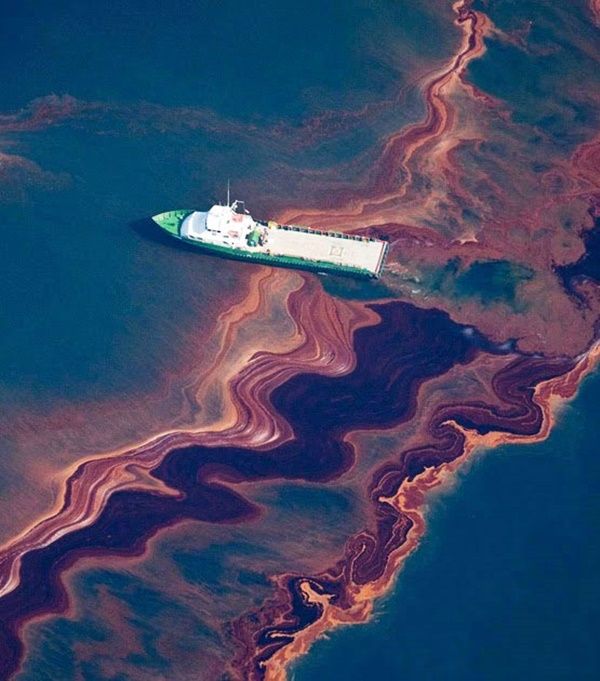


Radioactive substances:
Radioactive waste is any pollution that emits radiation beyond what is naturally released by the environment. It’s generated by uranium mining, nuclear power plants, and the production and testing of military weapons, as well as by universities and hospitals that use radioactive materials for research and medicine. Radioactive waste can persist in the environment for thousands of years, making disposal a major challenge. Accidentally released or improperly disposed of contaminants threaten groundwater, surface water, and marine resources.
Agricultural:
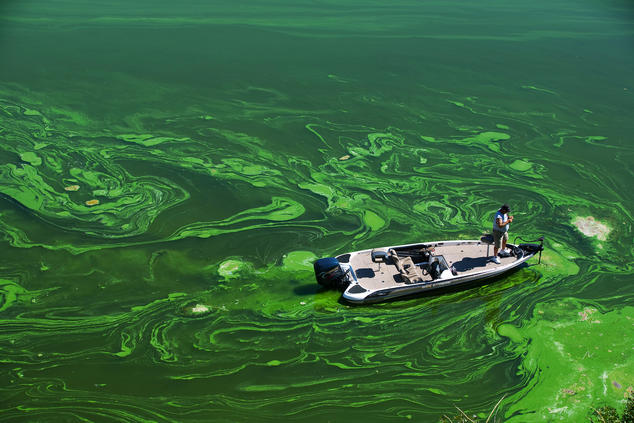
Not only is the agricultural sector the biggest consumer of global freshwater resources, with farming and livestock production using about 70 percent of the earth’s surface water supplies, but it’s also a serious water polluter. Around the world, agriculture is the leading cause of water degradation. Agricultural pollution is the top source of contamination in rivers and streams, the second-biggest source in wetlands, and the third main source in lakes. It’s also a major contributor of contamination to estuaries and groundwater. Every time it rains, fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste from farms and livestock operations wash nutrients and pathogens—such bacteria and viruses—into our waterways. Nutrient pollution, caused by excess nitrogen and phosphorus in water or air, is the number-one threat to water quality worldwide and can cause algal blooms, a toxic soup of blue-green algae that can be harmful to people and wildlife.


What Can You Do to Prevent Water Pollution?
With your actions
It’s easy to tsk-tsk the oil company with a leaking tanker, but we’re all accountable to some degree for today’s water pollution problem. Fortunately, there are some simple ways you can prevent water contamination or at least limit your contribution to it:
- Reduce your plastic consumptionand reuse or recycle plastic when you can.
- Properly dispose ofchemical cleaners, oils, and non-biodegradable items to keep them from ending up down the drain.
- Maintain your car so it doesn’t leak oil, antifreeze, or coolant.
- Don’t wash your car with open water shower.
- Adopt Landscaping that reduces runoff
- Avoid applying pesticides and herbicides. Use natural insecticides
- Reuse water as much as possible
- Conserve rooftop rainwater after due filtration in tanks and wells.
- Treat your waste water if you are not connected in sewage grid
- Ensure Zero leakage in your taps
- Divert surface runoff to dedicated reservoirs for later use
- Build small dams, hold water, recharge dug wells and make small Ponds
Water level is going low, why are we slow;
Save Rain Water!
Vardhman Envirotech,
India’s Passionate Rainwater Company.
